Galaxy Installation with Ansible
Contributors
| Author(s) |
|
| Editor(s) |
|
Questions
How does it all connect?
What steps will we go through?
Objectives
Get a high-level overview of a Galaxy server setup
last_modification Published: Feb 4, 2020
last_modification Last Updated: Apr 16, 2023
Install PostgreSQL & Galaxy extensions

Speaker Notes
- The first step of a Galaxy deployment is the database.
- This is the foundation of everything.
Install Galaxy & Attach Storage
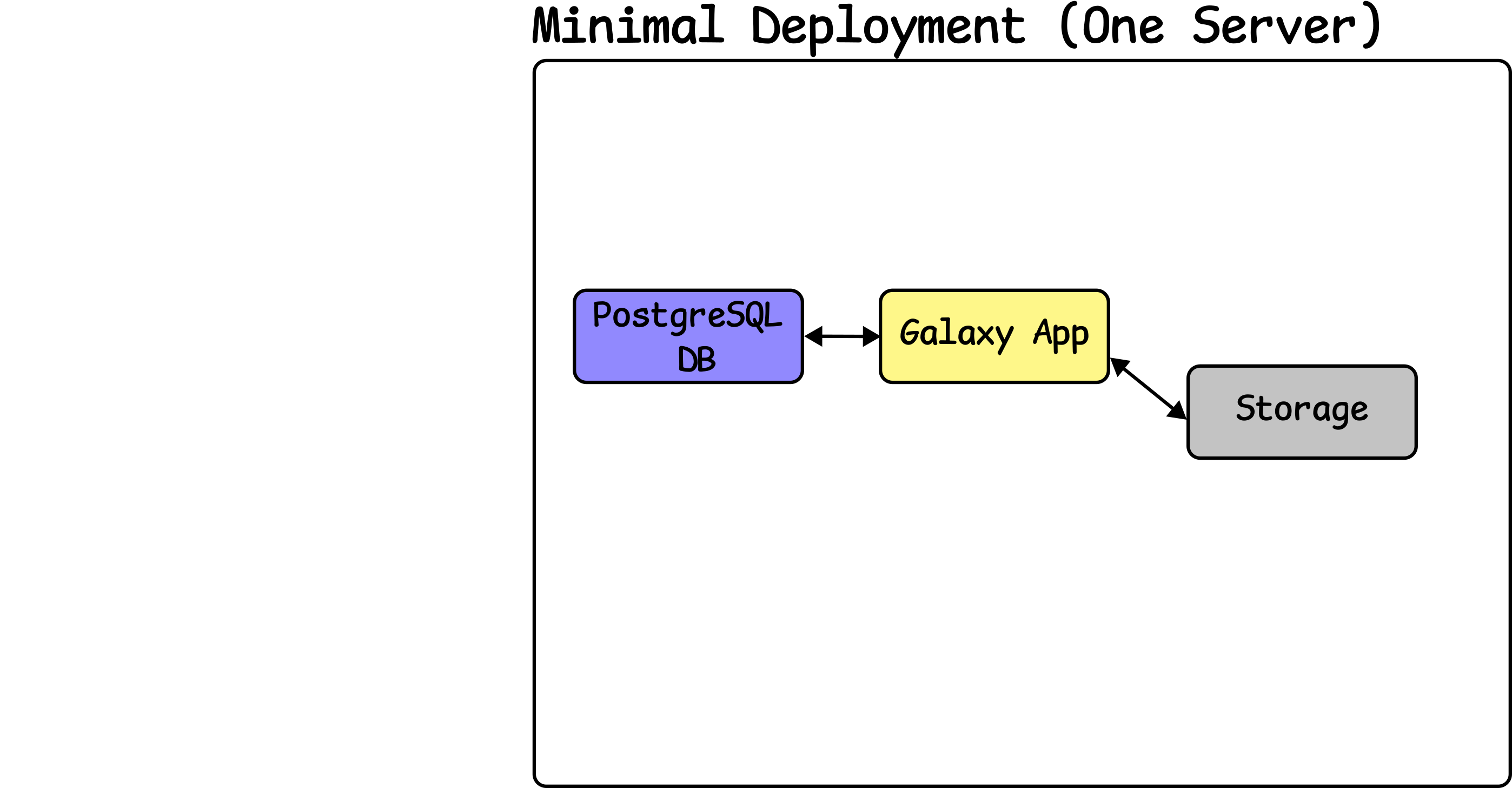
Speaker Notes
- Galaxy is deployed, and attached to the database.
- Storage must be available for Galaxy
Setup Gunicorn
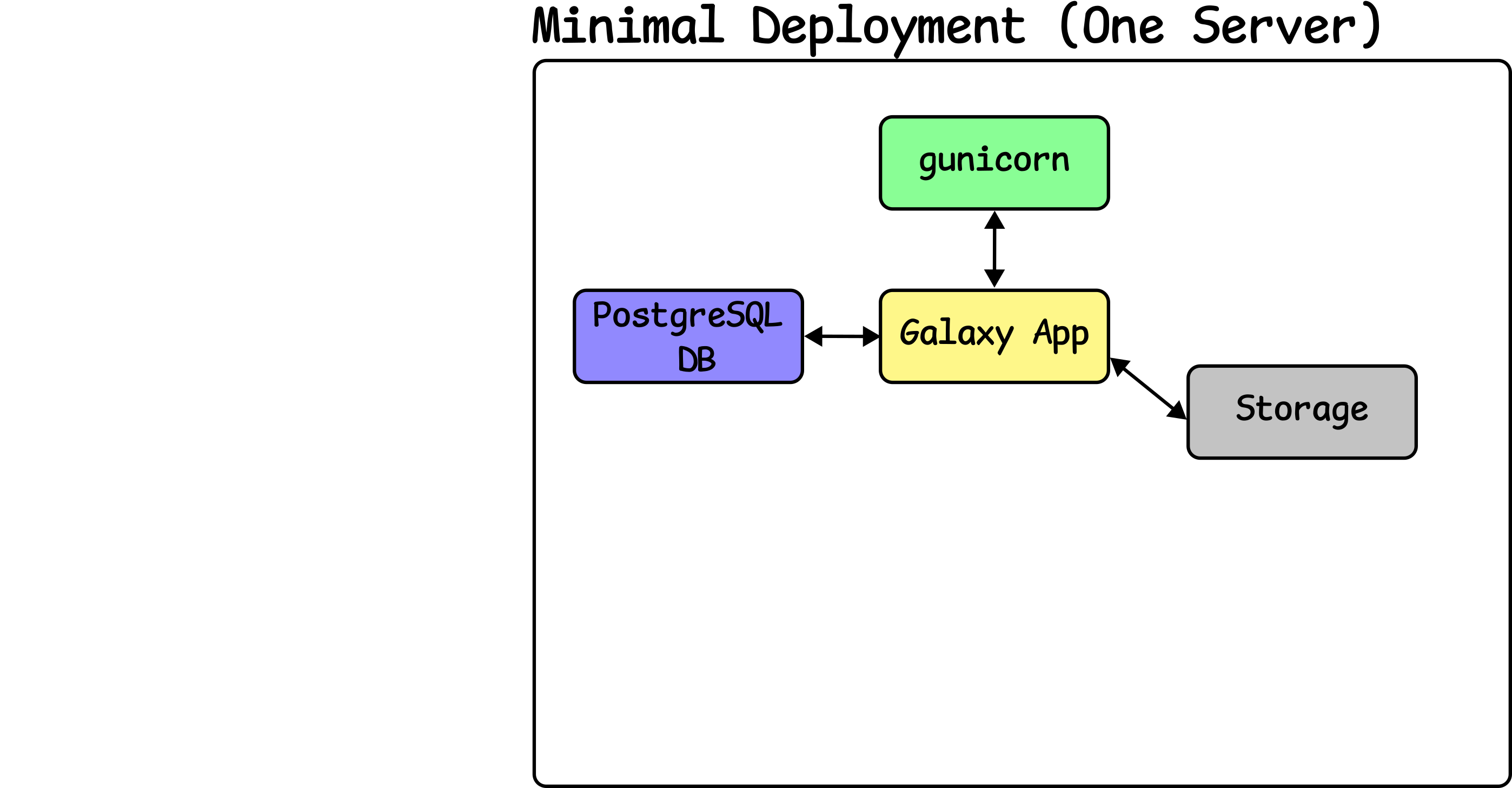
Speaker Notes
- Next, Gunicorn is setup to run the Galaxy app.
Configure NGINX
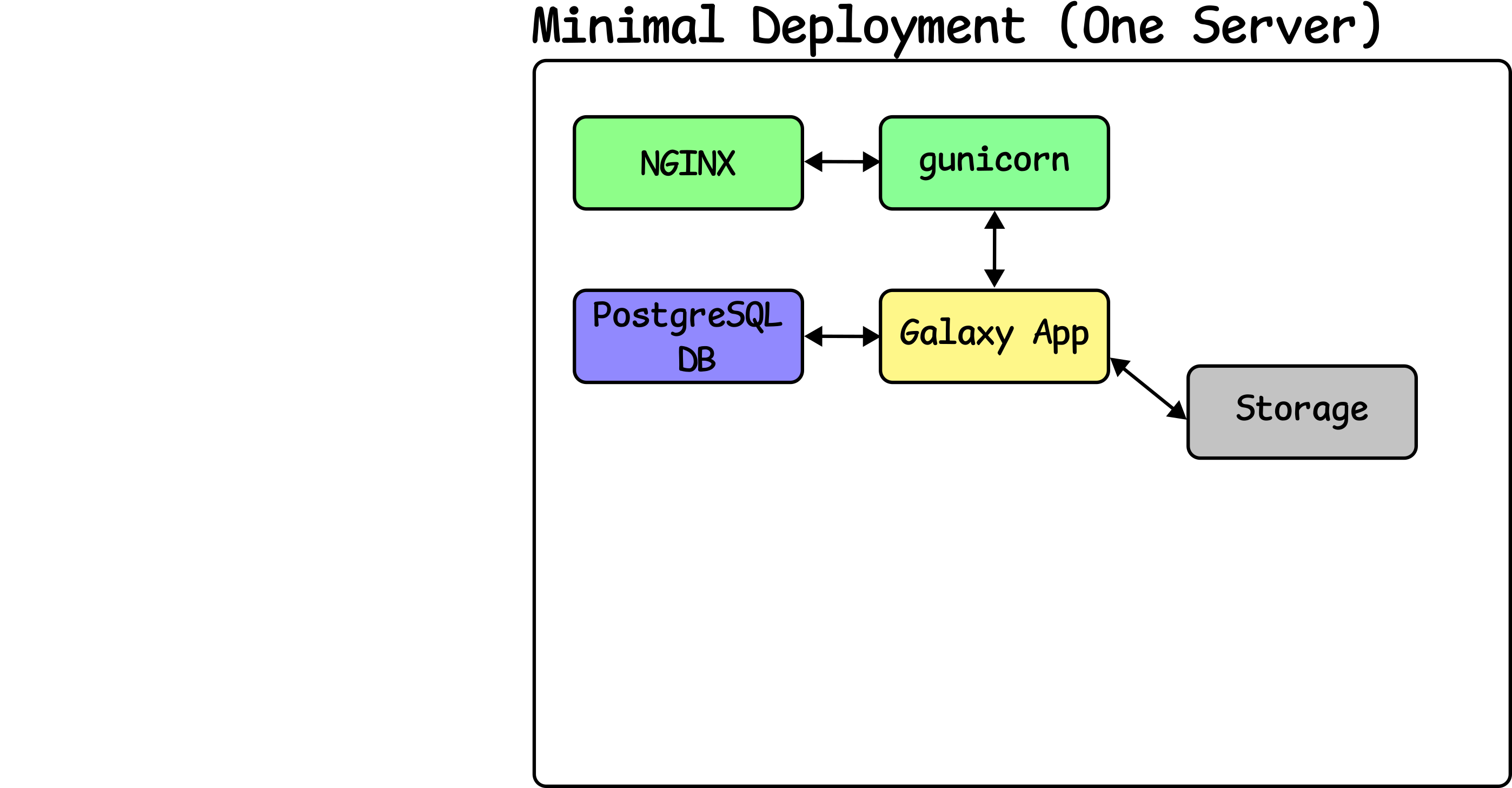
Speaker Notes
- Next, nginx is attached to UWSGI to proxy connections and speed up access.
Configure Backup
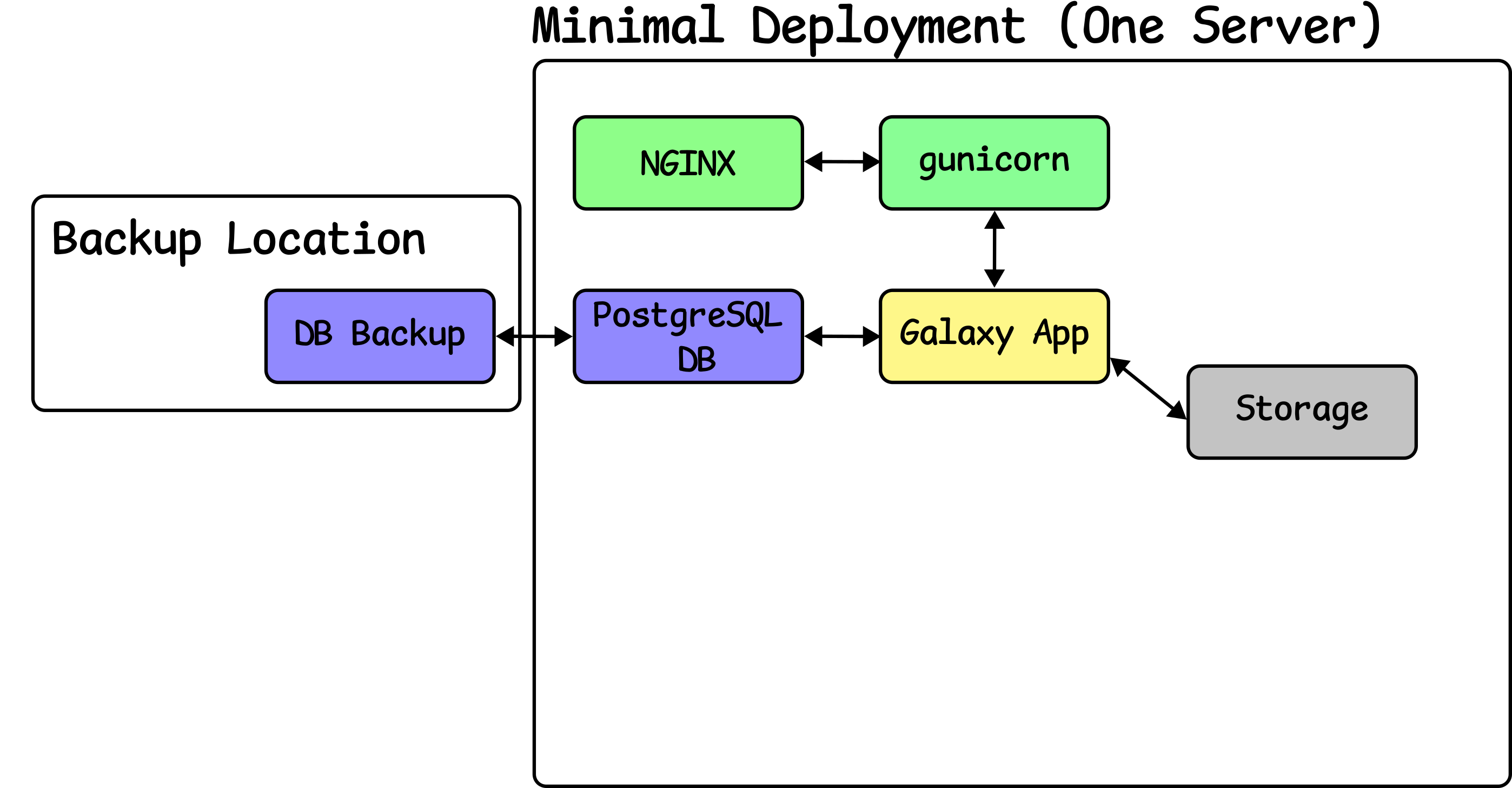
Speaker Notes
- A backup location is a very important part of a Galaxy deployment.
- We only backup the database, as the Galaxy configuration is stored in your playbooks
- You probably also want to backup the user data storage.
Configure CVMFS
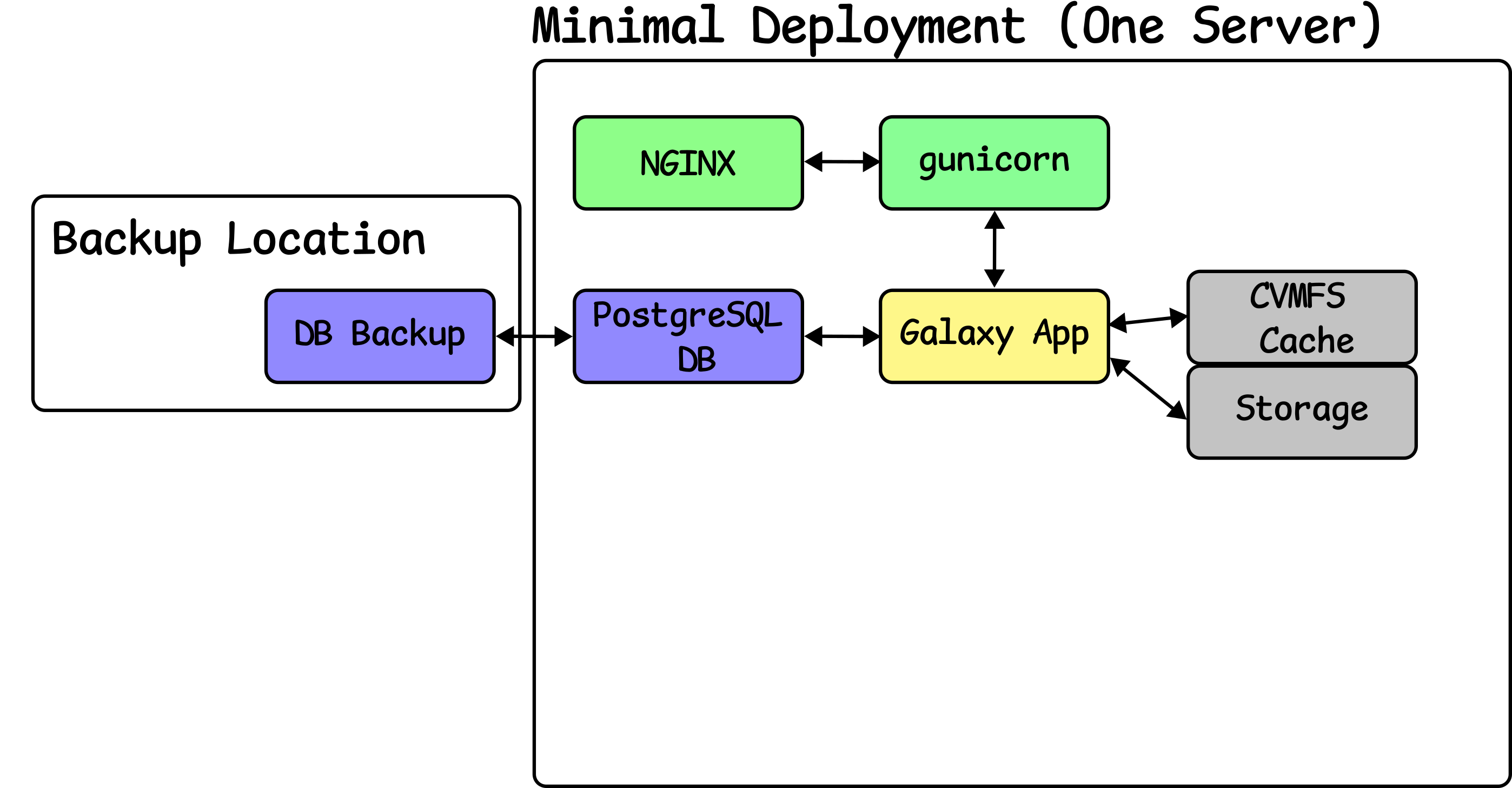
Speaker Notes
- CVMFS provides reference data and can be attached to your storage.
- Galaxy is configured to read data from CVMFS.
- Compute is configured to access it as well for jobs that need reference data.
Configure Job Handlers
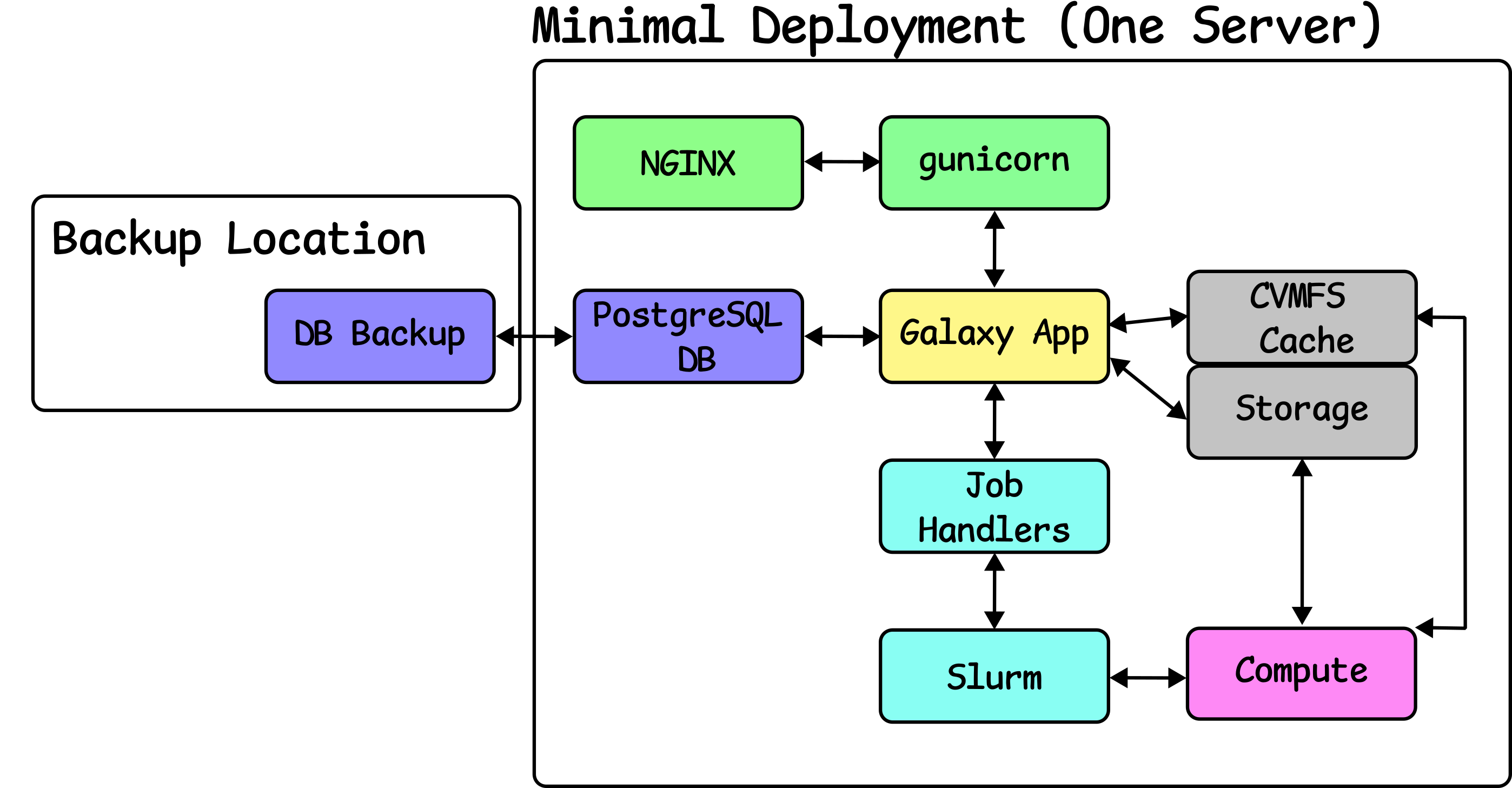
Speaker Notes
- Job handlers are configured and deployed with the app.
- These connect to the compute and manage jobs.
- Slurm is a much more intelligent resource manager than Galaxy.
- The job handlers are configured to connect to Slurm.
- Slurm deployment is explained in a separate tutorial.
Setup Remote Compute
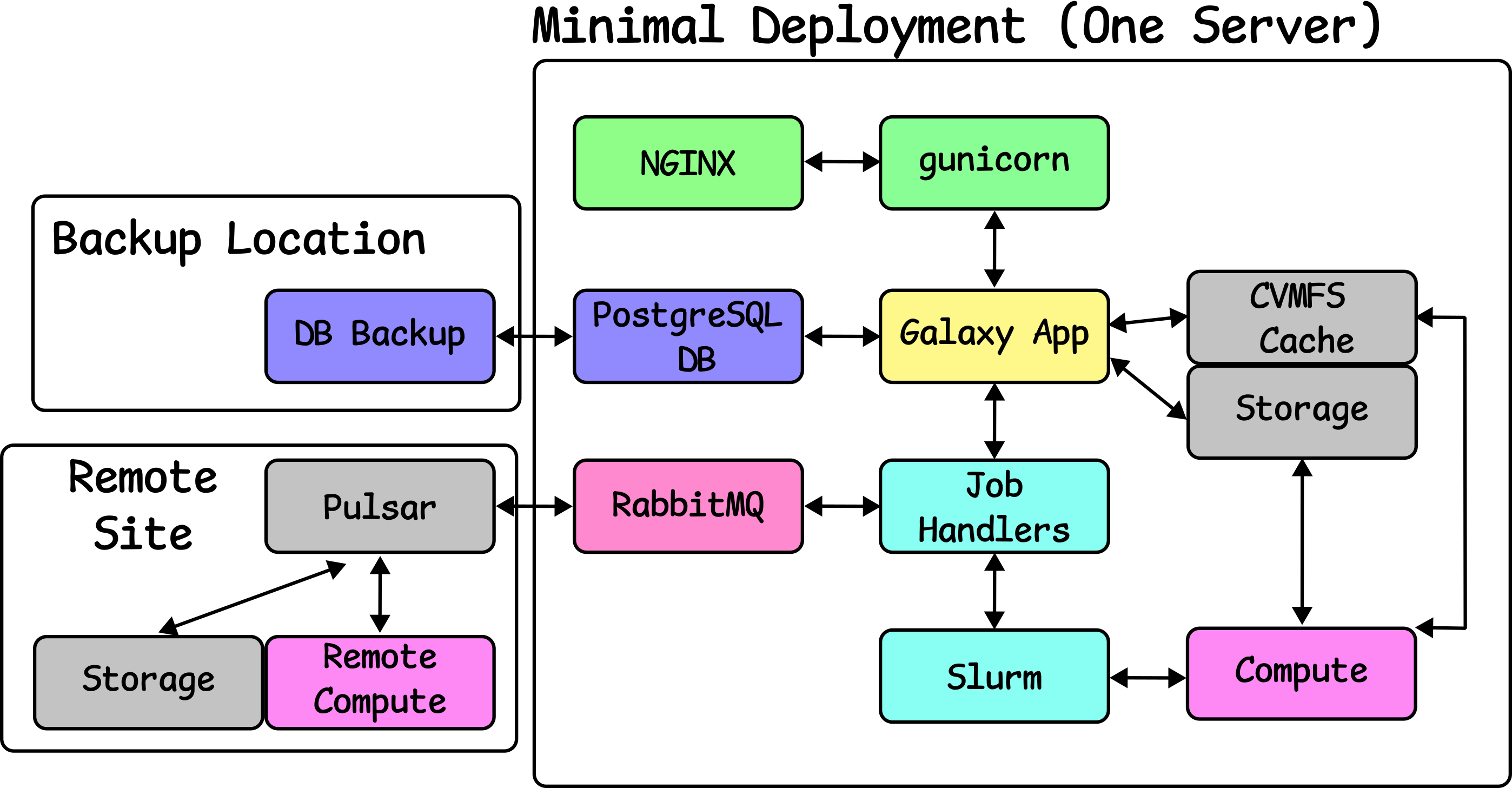
Speaker Notes
- Lastly, we can scale Galaxy further with remote compute.
- Pulsar connected at a remote site will handle this.
Major Initial Decisions
- Where to install Galaxy
- Where to store Galaxy datasets
- Database location
Speaker Notes
- These are the major initial decisions you will face.
- Where to install Galaxy, what servers or VMs do you have available?
- Where to store the data?
- Do you have enough space for your users?
- Where to reliably store the database?
Where to install Galaxy
- Must be at same path on cluster - more on this in cluster sessions
Speaker Notes
- Galaxy should be installed somewhere that is available across the cluster.
- We’ll cover this in detail in the lesson.
Where to store Galaxy datasets
- Must be at same path on cluster
- Consider future scalability
Speaker Notes
- Where should data be stored?
- Do you have network-attached storage available?
- It must be available to the entire cluster where compute happens.
Database location
- Fast local, reliable storage
- Consider future scalability
Speaker Notes
- The database server should be very reliable.
- It does not need so much disk space, but consider future scalability.
Basic best practices
- Run as an unprivileged user
- When possible, separate code from data and configs
- Write protect code and configs
.left[All of these practices are supported in the galaxyproject.galaxy Ansible role and covered in the Galaxy Installation with Ansible tutorial!]
Speaker Notes
- Here are the basic best practices.
- Run without privileges so if someone gains access they are limited in what they can do.
- Ensure the code and configuration are separate.
- If someone manages to act as the galaxy user, this will prevent them from changing galaxy’s behaviour.
- All of these best practices are built into the ansible role.
Example “Advanced” UseGalaxy.* Deployment
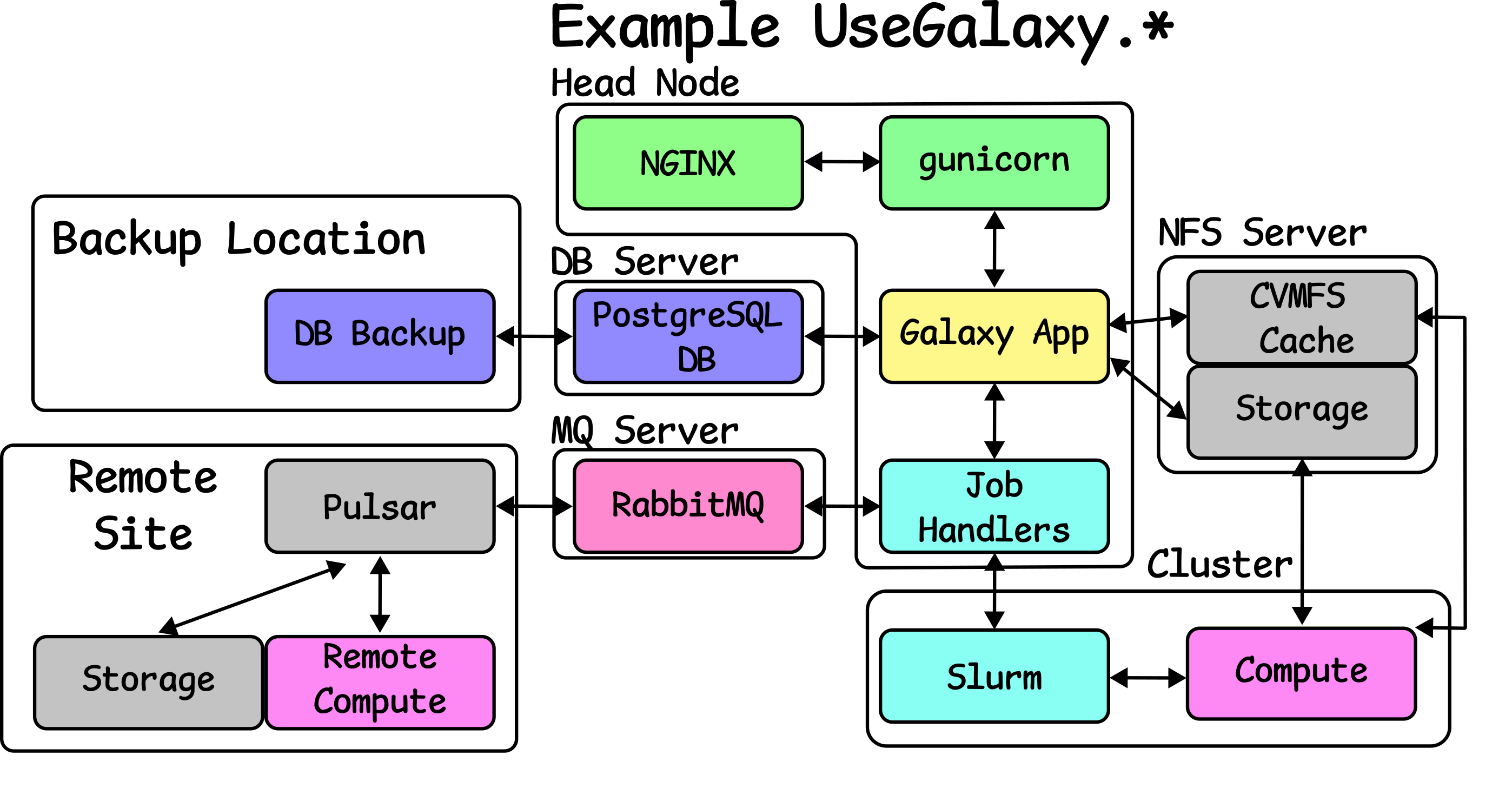
Speaker Notes
- Here we can see what a UseGalaxy.* deployment looks like
- This is roughly representative of UseGalaxy.eu, but all Galaxies are slightly different.
- For instance some Galaxies have multiple head nodes to balance the load.
Key Points
- Everything can be accomplished with Ansible roles from Galaxy
- You can easily deploy a base Galaxy, or one with more features.
Thank you!
This material is the result of a collaborative work. Thanks to the Galaxy Training Network and all the contributors! Tutorial Content is licensed under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Tutorial Content is licensed under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.